ABRASIVES
Topics discussed
- Definition
- Classification with examples
- Mohs Scale
- Applications
- Natural abrasives
- Synthetic abrasives
Throughout history, humans have used materials ranging from beach sand to walnut shells to paper bags as abrasives . Widely-used naturally occurring abrasives include garnet, cerium oxide, flint, emery, corundum (aluminum oxide), and diamond. These materials may have varying characteristics and chemical compositions depending on the specific geological source. Manufactured versions of these materials are usually more consistent in chemical composition and other characteristics. Abrasives can be distinguished in a variety of ways based on their hardness / color/ chemical composition / crystal shape etc to name a few.
Since the chemical composition- that is, the type of material- determines the abrasiveness, the identification of abrasives based on composition is popular
Definition
Abrasive is a substance used to wear down ( cut / polish / grind /sharp) the surface of the materials with which it is in contact
Abrasion is the ability of a substance to wear or tear the surface of other substance
Abrasives should possess good hardness, toughness and refractoriness
Hardness: Is defined as the ability of a substance to resist scratching
Toughness: Is defined as the ability of a substance to cause indentation or to scratch other material
Refractoriness: Is defined as the ability of a substance to withstand high temperature (Frictional Heat)
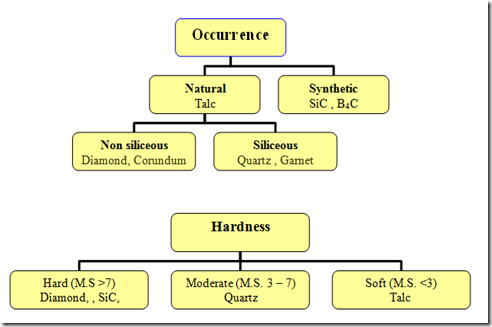
Abrasives are classified
Based On Occurrence : Natural and Synthetic
Based on Hardness: Hard ,Moderate and Soft
Mohs Scale - Mineral Hardness
The Mohs scale of mineral hardness was devised by Frederich Mohs, a German mineralogist in 1812.
To devise the scale, he selected ten minerals as a basis because they were common or readily available, thus the scale is not linear, but is a bit arbitrary.
It is a measure of the relative hardness and resistance to scratching between minerals (tested by Pin on Disc method)
Though there are other scales like Rockwell, Vickers and Brinell, Mohs scale is still the most common scale of mineral hardness.
Moh’s scale
| Mineral | Moh’s scale | composition |
| Talc | 1 | Mg3Si4O10(OH)2 |
| Gypsum | 2 | CaSO4.2H2O |
| Calcite | 3 | CaCO3 |
| Fluorite | 4 | CaF2 |
| Apatite | 5 | CaF2.3Ca3(PO4)2 |
| Feldspar | 6 | K2O.Al2O3.6H2O |
| Quartz | 7 | SiO2 |
| Topaz | 8 | AlF3.SiO2 |
| Corundum | 9 | Al2O3 |
| Diamond | 10 | C |
Mnemonics to remember the order of Mhos scale
To Get Candy From Aunt Fanny Quit Teasing Cousin Danny
Mohs scale of common household substances
(Just for information – do not memorise)
| Material | Hardness |
| Plastic | 1 |
| Salt | 2.3 |
| Fingernail | 2.5 |
| Gold , Silver | 2.5-3.0 |
| Copper coin | 3.5 |
| Platinum | 4 – 4.5 |
| Window glass | 5.5 |
| Steel File | 6.5 |
| Ceramic tile | 7.0 |
Natural Abrasives
Corundum (Al2O3) [Alundum]
Properties :
Crystalline
Very Hard
Moh’s scale-9
brown to grey in colour
Corundum is used in :
In grinding wheels
To grind glass/lens/metals,
Ruby lasers
Diamond (C)
Diamond exist in three major forms
Diamond (gem grade)
Borts – These are diamonds that are off colour or faulty
Carbonado – These are black diamonds mined from Brazil. They have good hardness, but due to lack luster, do not find application as jewelry.
They are commonly used as abrasives
Abrasive grade diamond has the following properties
crystalline
Chemically inactive
Moh’s scale-10
Uses
In bits of drilling points
Saw teeth for cutting rocks
In grinding wheels
In engraving tools
Emery
Composition
Alumina (crystalline) 50 - 75% Magnetite 20 - 40% Other minerals 12 %
Properties
Dark grey to black
Hardness depends upon alumina content
Moh’s scale - 8
Uses
In emery paper and cloth used for polishing.
In bits of cutting and drilling tools
Garnets
Properties
Tri silicates of alumina/ magnesia/ ferrous oxide.
Common garnet- Calcium alminium iron silicate
Moh’s scale 6 -7.5
Uses
To paper/cloth to polish wood /metals,
As bearing pivots in watches
In glass grinding
Quartz (SiO2)
Properties
SiO2 (pure crystalline)
Moh’s scale – 7
Hydrated form of SiO2 is called Flint
Uses
Impure grey quartz used in sand paper
As granules in grinding
Machines used to grind flour, pigments & ores.
Synthetic Abrasives
Silicon Carbide / Carborundum / Crystolon (SiC)
Preparation
Raw materials are
i. Petroleum Coke (source of carbon)
ii. Sand (source of Si)
iii. Saw Dust ( To provide hardness)
All raw materials are sized, dried and mixed along with old charge and fed into the Acheson furnace with little amount of NaCl (flux)
Properties
M.Pt. is 2700oC
Mohs scale hardness is 9.3
Chemically Inert
High Thermal Stability
Brittle hence strength is less
USES
Cutting tools
Grinding of cast iron, brass, bronze , porcelain marble
Polishing leather, lenses (Abrasive paper and Cloth)
Refractory in furnace
Boron Carbide / Norbide (B4C)
Preparation
i. Petroleum Coke (source of carbon)
ii. Boron Oxide
iii. Saw Dust (To provide hardness)
All raw materials sized, dried and mixed along with old charge and fed into the
Acheson furnace with little amount of NaCl (flux).
Properties
Moh’s scale hardness - 9 . 7
Chemically inert
Resist oxidation more than diamond.
Uses
Grinding dies
Cutting
Sharpening hard high speed tools
Advantages of Synthetic Abrasives
Unlike natural abrasive synthetic abrasives possess uniform chemical composition
Due to uniformity in the composition the hardness at various points also remain uniform
Important General Applications of Abrasives
In grinding wheels (Bonded abrasives) abrasives are used to grind and polish the surface of metals and composites ,sharpen tools like knife ,saw tooth etc.,
In the form of paper / cloth (abrasive coated on paper / cloth with the help of glue) abrasives are used for cleaning and polishing soft and precious metals (Au, Ag, W etc.,) .They are also used to shine leather, clean lens , windscreen etc.,
In few places abrasives are used in the form of loose powder-for polishing hard metal and wood
Cleaning products also contain abrasives suspended in a paste or cream.
For example tooth paste contains calcium carbonate / silica /mica as a "polishing agent" to remove plaque and other matter from teeth as the hardness of the abrasive used is less than that of tooth enamel but more than that of the contaminating agent(plaque material).
Abrasives may also be used to prepare surfaces for application of paint and varnish
Pumice stone ( abrasive) is used to remove dead cells from skin (usually to keep the feet crack free)
Soft abrasives are used in cosmetic industries in various products to rejunivate skin and maintain a smooth and silky texture








The preparation programs offered by these foundations are endeavors at giving many qualified instructors to educate in the schools. The National Accreditation Board authorizes educator preparing programs so as to guarantee quality.
ReplyDeleteijazah course
The idea of home chemistry tuition centre cost is expanding step by step in Singapore at a quick rate. The measure of cash spent by guardians for their kids each year on educational costs is disturbing which is expanding continually.
ReplyDelete